With the great development of productivity people’s living standards, industrial casters are increasingly wide range of applications. The following is about the structure and characteristics of various industrial casters:
First, the structure
Industrial casters are mainly composed of the following parts:
1. Wheel surface material: generally made of rubber or polyurethane and other materials, flexible and wear-resistant, used to contact the ground and bear the load.
2. Axle: the component that connects the tire to the caster bracket fixed to the equipment, which can be made of steel or other stronger metals.
3. Bearing: Used to reduce the friction between the tire and the axle to improve the rotational efficiency and life of the caster.
4. Bracket: the component that mounts on the equipment and secures the caster, it can be a single bracket or multiple brackets.
Second, several key points of casters
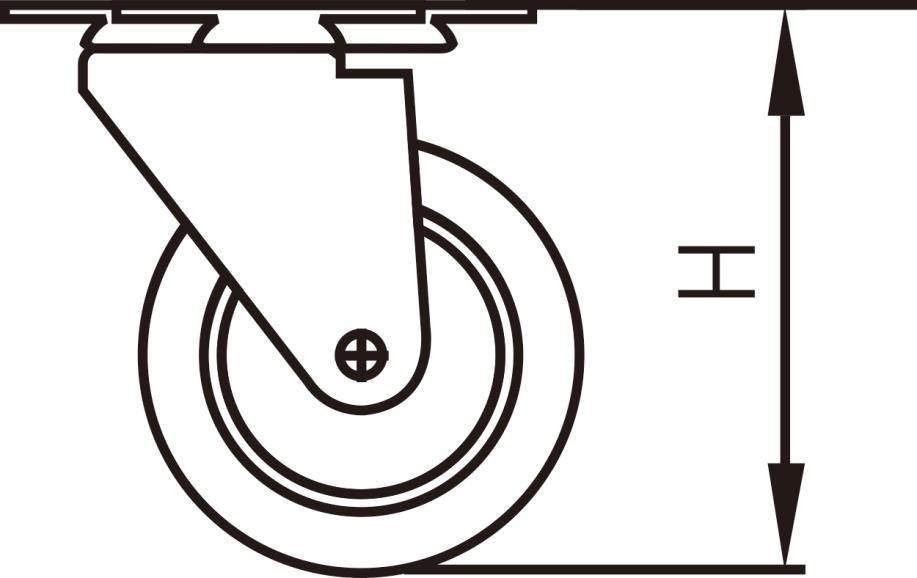
Installation height: refers to the vertical distance from the ground to the equipment installation position, the installation height of the caster is the maximum vertical distance from the caster base plate and the wheel side far.
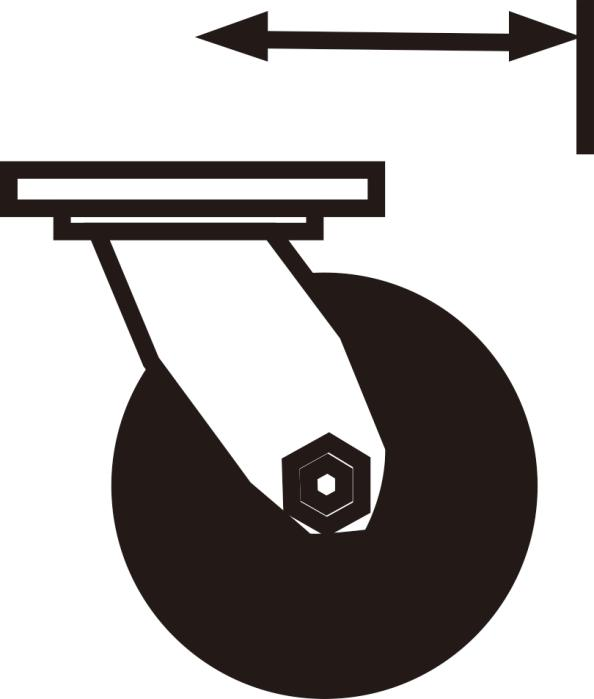
Bracket steering center distance: refers to the horizontal distance from the vertical line of the center rivet to the center of the wheel core.
Turning radius: refers to the horizontal distance from the vertical line of the center rivet to the outer edge of the tire, and the proper spacing enables the caster to turn 360 degrees. Whether the turning radius is reasonable or not directly affects the service life of the caster.
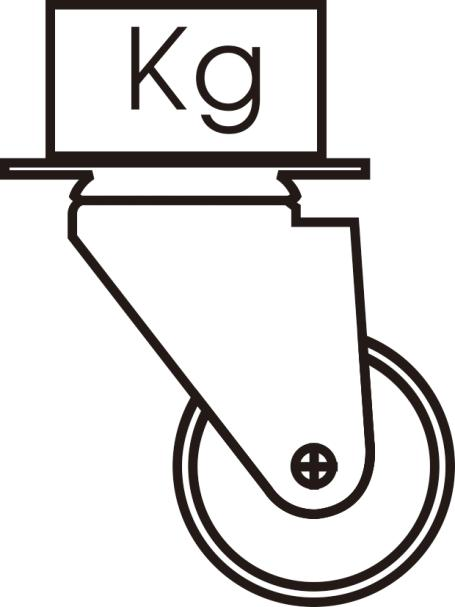
Traveling load: casters in the movement of the weight-bearing capacity is also known as the dynamic load, the dynamic load of the casters due to the factory’s test method is different, but also due to the different materials of the wheels are different, the key lies in the structure of the bracket and the quality of whether it is able to resist the impact and vibration.
Shock load: the instantaneous load-bearing capacity of the caster when the equipment is shocked or vibrated by the load-bearing object. Static Load Static Load Static Load Static Load: the weight that the caster can bear in the static state. Static load in general should be exercised for the load (dynamic load) of 5 to 6 times, static load should be at least 2 times the impact load.
Steering: Hard, narrow wheels are easier to steer than soft, wide wheels. Turning radius is an important parameter of wheel rotation, too short turning radius will increase the difficulty of steering, too large will lead to wheel shaking and shorten the life of the wheel.
Traveling flexibility: factors affecting the flexibility of the casters travel are the structure of the bracket and bracket steel selection, wheel size, wheel type, bearings, etc., the larger the wheel traveling flexibility is better, in the smooth ground on the hard, narrow wheels than the flat side of the soft wheels to save energy, but in the uneven ground on the soft wheels to save energy, but in the uneven ground on the soft wheels can better protect the equipment and shock absorption.
As the originator of manganese steel casters, the industrial casters produced by JOYAL manganese steel casters are labor-saving and durable, and can efficiently solve the handling problems of enterprises. Made of manganese steel, more labor-saving, Zhuo Ye would like to work together with you!
Post time: Nov-14-2023